Air-Conditioning Systems from Eberspaecher for Articulated Busses in São Paulo
- Eberspaecher is reliable partner for bus air-conditioning systems in Brazil
- Already around 800 articulated busses in São Paulo are equipped with air-conditioning systems from Eberspaecher
- More than 200 air-conditioning systems type AC353 for new articulated busses in São Paulo
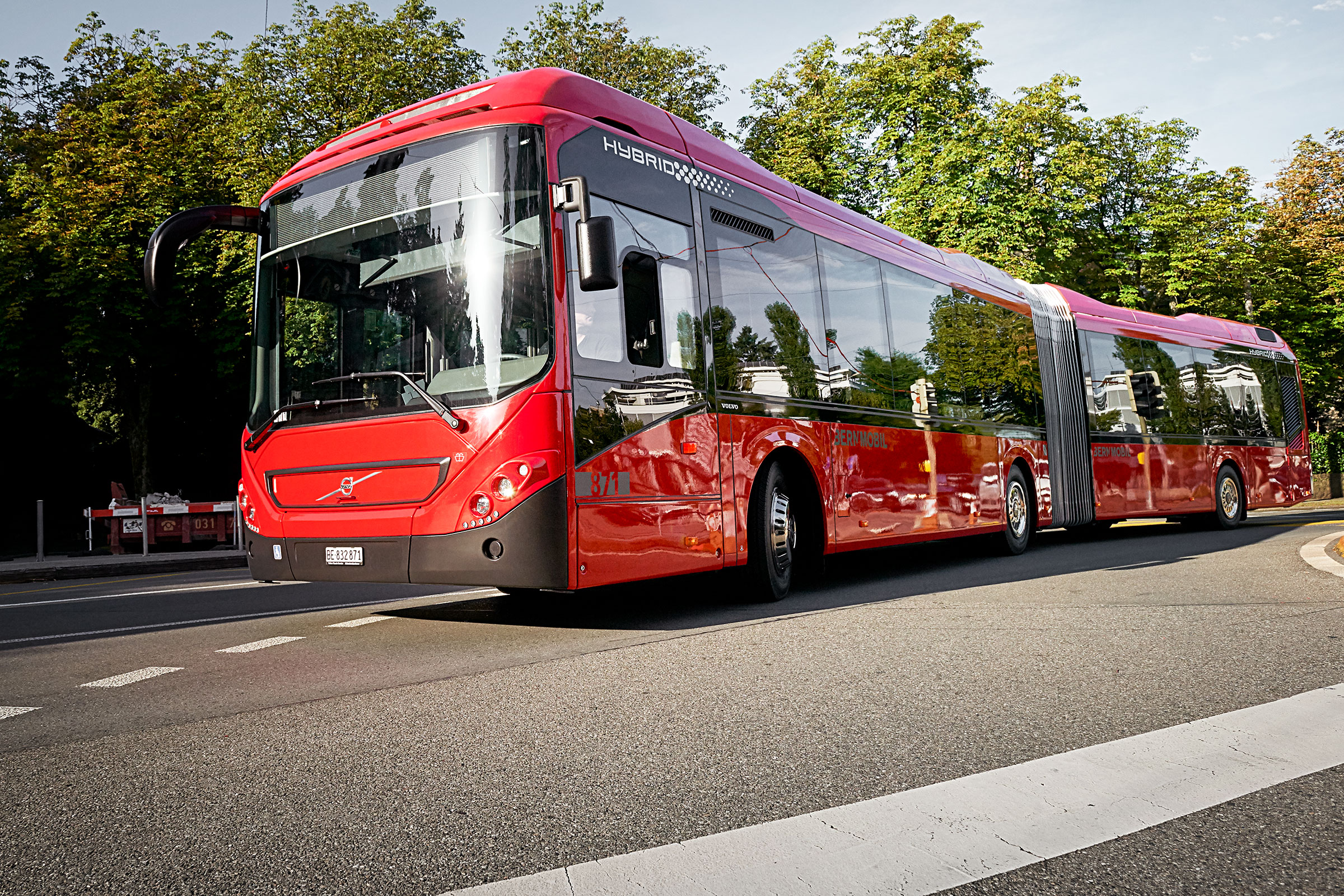
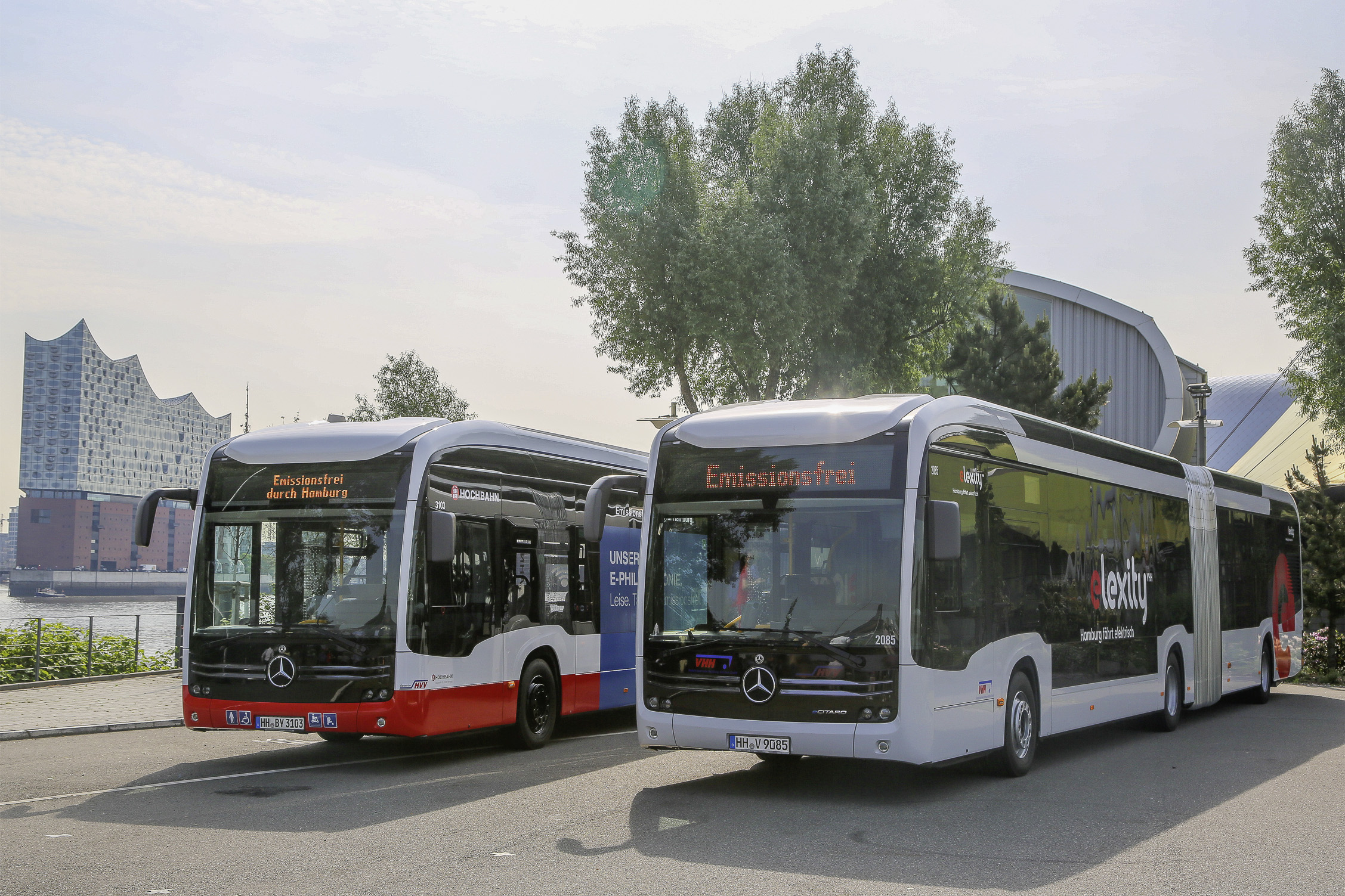
For many years, Brazilian fleet operators and bus manufacturers have relied on bus air-conditioning expertise of Eberspaecher: In São Paulo, the German thermal management expert has already equipped nearly 800 articulated buses with air-conditioning systems. Another 150 units were installed in the past 12 months and are already in operation in the city of São Paulo. More than 60 additional units will follow in the mid of 2021.
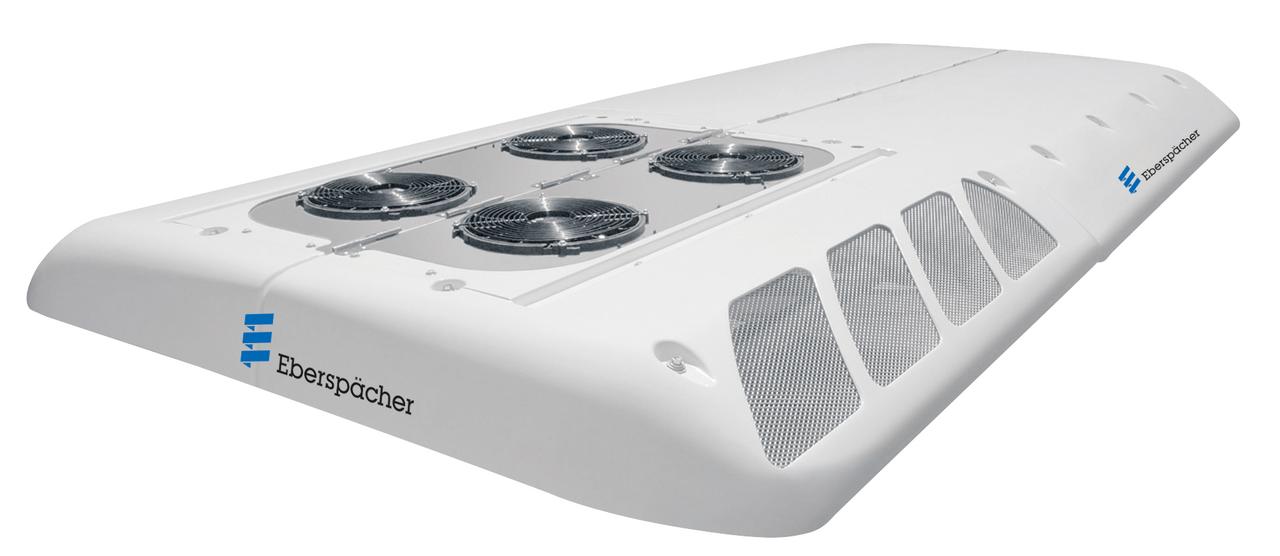

The articulated city busses are equipped with the AC353 inline roof-mounted AC system product platform, which has a very high global reliable reputation. The system comes in various cooling capacity classes and impresses fleet operators and manufacturers through long lifetime and its service friendliness. Passengers enjoy the high comfort level and pleasant temperatures the AC353 product family provides during the usage of public transport buses. The AC353 air-conditioning systems can also be combined with Eberspaecher’s clean air solutions for efficient air filtration, air purification and air sterilization.
Eberspaecher’s Bus & Coach Business Unit offers heating and cooling solutions for every kind of busses and coaches. No matter the requirements, bus and drive type – the German air conditioning specialist offers the optimum solution. Customers all over the world particularly appreciate the flexibility, reliability, and efficiency of air-conditioning systems from Eberspaecher.
The systems from Eberspaecher Climate Control Systems Bus & Coach for the South American market are manufactured in Sorocaba, Brazil. More than 20 employees produce bus AC systems in this plant. The worldwide Eberspaecher dealer network ensures optimum service throughout the life-cycle duration.
This article was originally published by Eberspächer.